Module 3: Data Preparation with Power Query
Introduction To Power Query
Power Query is a data connection technology that enables you to discover, connect, combine, and refine data across a wide variety of sources. It is available in several Microsoft products, including Power BI, Excel, and Microsoft Dataverse.
- Extract - retrieve data from a wide variety of sources.
- Transform - Data cleaning, shaping, and transforming data to meet your analysis needs.
- Load - Load the transformed data into the desired destination.
Destinations might be Semantic Models, pivot tables or a data lake
Power Query can derive data from other types of data.
In BI, use the Transform Data button to open Power Query Editor.
Abbreviations can be fixed - USA to United States of America, Weds to Wednesday. Remove unnecessary columns, filter rows, change data types, merge tables, and create calculated columns. Calculate dates, extract parts of text, and perform aggregations.
Power BI will always use Power Query to prepare the data for analysis.
Understanding the Power Query Editor Interface
Click on Transform Data to open the Power Query Editor.
The Power Query Editor interface consists of several key components that help you navigate and manage your data transformation tasks.
- Ribbon - The ribbon at the top of the interface contains various tabs and commands for performing data transformation tasks. It includes options for data manipulation, formatting, and other operations. Note that the ribbon is divided up into all table, text, and date tools, depending on the type of data you are working with.
- Queries Pane - The Queries pane on the left side of the interface displays a list of all the queries in your Power BI file. You can select a query to view and edit its data. You can also create new queries, duplicate existing ones, and manage query dependencies.
- Data Preview - The central area of the interface shows a preview of the data in the selected query. You can use this area to explore the data, apply transformations, and see the results in real-time.
- Applied Steps Pane - The Applied Steps pane on the right side of the interface shows a list of all the transformations that have been applied to the selected query. You can click on each step to view its details, modify it, or delete it if necessary. The gear icon allows you to edit the settings of a specific step.
- Formula Bar - The formula bar above the data preview area allows you to view and edit the M code for the selected query. M code is the language used by Power Query to define data transformations
- Status Bar - The status bar at the bottom of the interface provides information about the current state of the query, such as the number of rows and columns in the data preview.
Loading and cleansing data with Power Query
- Source
- Navigation
- Other steps
Transform Data
Fix rows and columns
- Remove columns
- Remove rows
- Rename columns
- Change data types
- Split columns
- Merge columns
- Pivot columns
- Unpivot columns
- Replace values
- Fill down/up
- Sort rows
- Group by
- Transpose etc etc etc :)
Note: Use First Row as Headers is a fun thing to use.
Tip: Null values can be replaced with 0 or other values. Tip: Fill up or fill down can be used to fill in missing values based on adjacent cells up or down.
Transforming and Deriving new Data
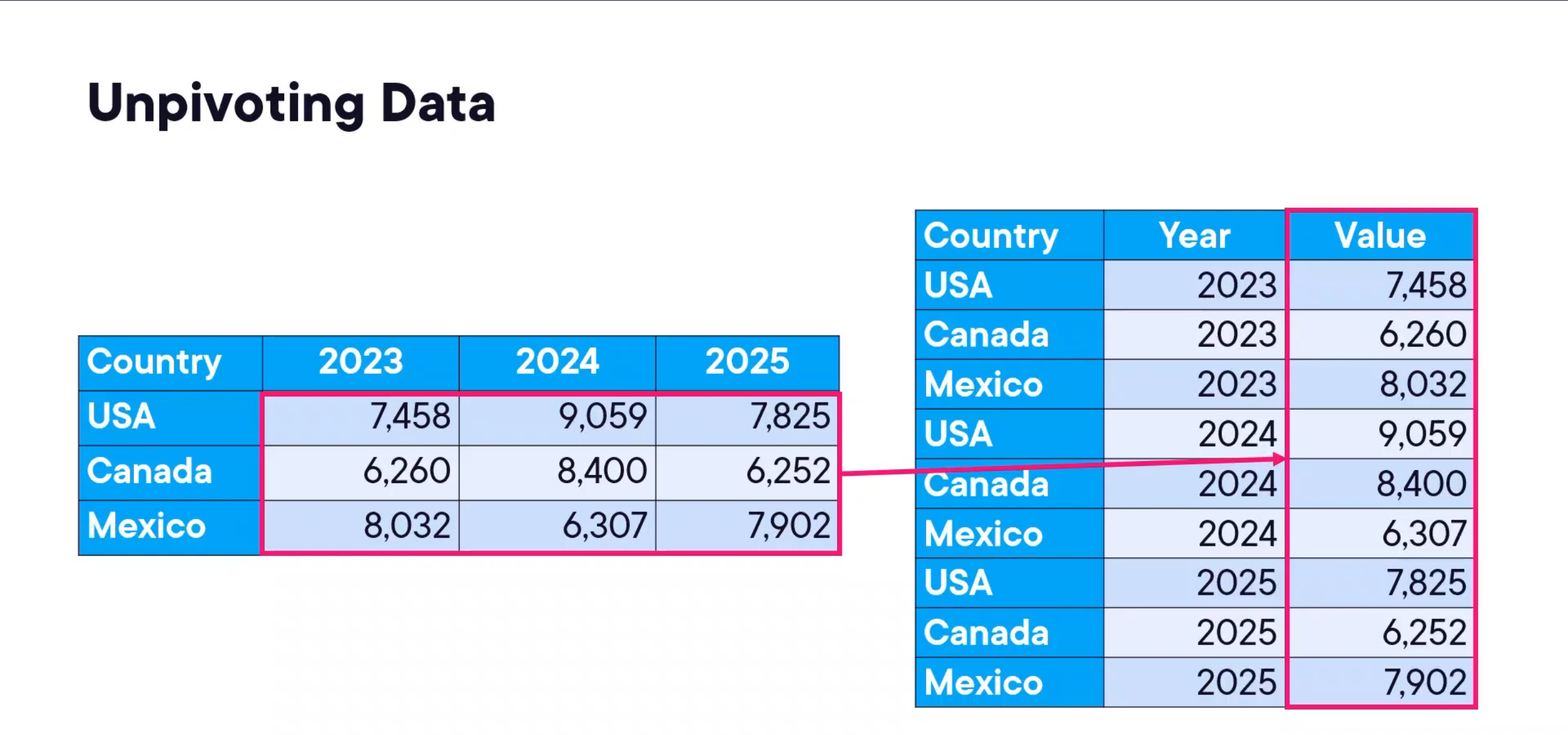
Unpivoting Data: Otherwise known as flattening or normalizing data. This is useful when you have columns that represent values that should be in rows.
Splitting Columns
Splitting columns can be done by delimiter, number of characters, or by positions.
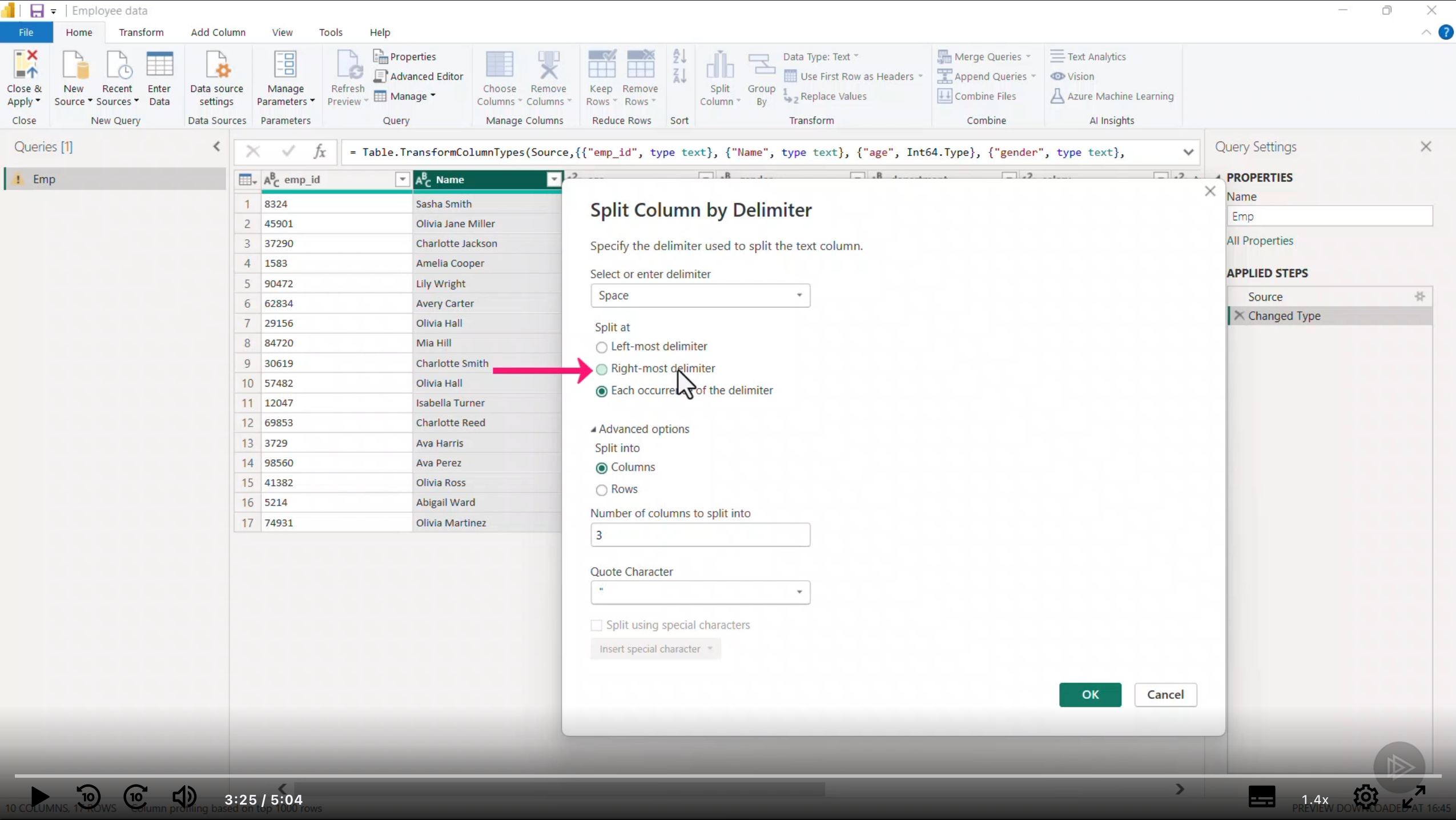
Sometimes splitting columns can result in size savings. For example, splitting a full name into first and last name can save space if you only need one of the names for analysis. Or on dates, if you have date and time in one column, splitting them can allow you to analyze just the date or just the time, and only have 365 dates (days in a year) instead of thousands of date-time combinations.
Append and Merge
Append - stacking tables vertically Merge - joining tables horizontally
3 CSVs for each day, this just adds the data at the bottom.
Merging will add those to different columns instead of rows. (vLookup)
Combining data with Append and Merge
Duplicating Queries
You can duplicate a query to create a copy of it. This is useful when you want to create a new query based on an existing one without modifying the original.
- A reference query creates a new query that references the original query. This means that any changes made to the original query will be reflected in the reference query.
- A duplicate query creates a completely independent copy of the original query. Changes made to the duplicate query will not affect the original query.
Errors with Power Query
- Data Source or Data errors
- Type Mismatches
- Missing Values
- Date/Time Errors - may want to coordinate UTC vs local time
- Formula Errors - check the formula bar for M code issues
Data Source or Data errors
These errors occur when there is an issue with the data source or the data itself. Common causes include:
- Connection issues - network problems, incorrect credentials, or changes to the data source.
- Data format issues - unexpected data types, missing columns, or inconsistent data structures.
- Someone deleted or moved or renamed or changed something someplace. Tip: The query dependencies view can help you understand how queries are related to each other.
Type Mismatches
These errors occur when there is a mismatch between the expected data type and the actual data type. For example, if a column is expected to contain numbers but contains text values, a type mismatch error may occur. To resolve type mismatch errors, you can:
- Change the data type of the column to match the expected type.
- Use the "Replace Errors" feature to replace invalid values with a default value.
- Use the "Remove Errors" feature to remove rows with invalid values. Tip: Data type detection only selects the first 1000 rows, so if there are outliers later in the data, they may not be detected correctly. Note, what if you concatenate a text column with a number column? The number needs to be converted to text.
Date/Time Errors
Date/time errors can occur when there are issues with date and time values in your data. Common causes include:
- Invalid date formats - dates that do not conform to the expected format.
- Out-of-range dates - dates that fall outside the valid range for date values.
- Time zone issues - dates and times that are not properly adjusted for time zones. Note: a common issue is MMDDYY vs DDMMYY :) To resolve date/time errors, you can:
- Change the data type of the column to Date/Time. Use the "Using Locale" option if the date format is specific to a certain region.
- Use the "Replace Errors" feature to replace invalid date values with a default date.
- Use the "Remove Errors" feature to remove rows with invalid date values.
- Use the "Transform" feature to adjust date and time values for time zones.
Tip: This is helpful when you want to harmonize date and time values from different time zones.
Handling Errors in Power Query
Power Query provides several features to help you handle errors in your data. Here are some common techniques:
- try...otherwise - This feature allows you to specify an alternative value or action to take when an error occurs. For example, you can use try...otherwise to replace error values with a default value.
- try catch - This feature allows you to catch specific types of errors and handle them accordingly. For example, you can use try catch to log error messages or send notifications when certain types of errors occur.
- Note: Try Catch is useful in Excel, not so much in Power BI.