Folder main Part 3: Secure your Data and Applications
Link:
Deploy and Secure Azure Key Vault
Objectives
- Define what a key vault is and how it protects certificates and secrets
- Deploy and configure Azure Key Vault
- Secure access and administration of your key vault
- Store keys and secrets in your key vault
- Explore key security considers like key rotation and backup/recovery
Explore Key Vault
- Secrets management
- key management
- certificate management
- HSMs
Standard and Premium skus - the biggest difference is that premium uses HSM protected keys. Check your contributor permissions as they can grant themselves access to the data planes and have access to the contents of the keyvaults.
Configure Key Vault Access
Access to a key vault is controlld through two interfaces:
- Management plane - create and delete key vaults, update access policies
- Data plane - add, delete, modify keys secrets and certificates You can use Entra ID for authentication to both, but needs set up in multiple locations.
- User plus application access - this application accesses Key Vault on behalf of a user = Application only access - the application itself is granted access to the key vault.
Single Mechanism for authentication to both planes has several benefits
- organizations can centrally control access to all key vaults
- if a user leaves, they lose access to all key vaults
- MFA and other custom authentication options
Review a secure Key Vault Example
This example consists of 4 key teams: Security - deploying the SSL Certificates, RSA keys, Storage Account keys Developers and operators - deploying the application Auditors - people who review the application to make sure it is running correctly Subscription Admin - gives out the roles to these teams
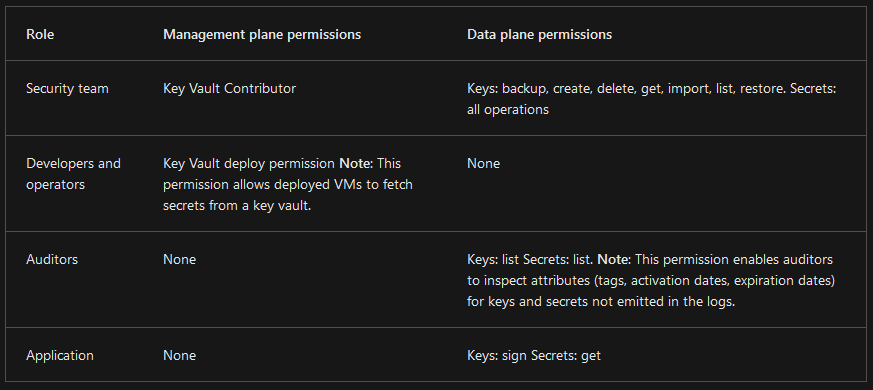
Deploy and manage key vault certificates.
Certificate policy must be created to dictate how the certificate is used. There is one instance of a policy with each individual certificate.
x509 certificates are generated from pem and pfx formatted certificates.
You need to register with a known certificate authority AND create credentials for KV to enroll certificates.
Certificate contacts for any type of action that requires a notification - anything todo with renewals
Certain access roles for key vaults that handle certificates exclusively rather than mixing other types of keys or secrets. The access policy is distinct for certificates than other types.
Create Key Vault Keys
Keys in the keyvault are represented as JSON Web Key objects (JWK)
- Soft keys - encrypted at rest in a vault using a key that is a HSM
- Hard keys - encrypted inside an HSM
Key Vault support many operations on key objects.
- Create
- Import
- Update
- Delete
Extra cryptographic operations
- Sign and Verify
- Key Encryption/Wrapping
- Encrypt and Decrypt
App service plans - key vault references are a way to introduce secrets management into your app without significant code changes. The system identity can fetch a secret and then make it available to the app as an environment variable.
BYOK: Hardware security module key-generation solution - you can add keys in HSMs that never leave the HSM boundary using Key Exchange Keys - KEKs
Customer managed keys
Need to rotate keys:
- As part of a manual process
- Programmatically by using REST API calls
- Through an Azure Automation script
Create new key and then revoke the old, making sure that the application can pick up and use the new key and not stuck on the old one, which no longer works.
Enable Key Vault Secrets
You can protect your keys by encrypting them before encrypting them in the vault.
The fields of the key vault secrets:
- Name-value pair - Name must be unique in the Vault
- Value can be any Unicode Transformation Format (UTF-8) string - max of 25 KB in size
- Manual or certificate creation
- Activation date
- Expiration date
ALL KEY VAULT SECRETS ARE ENCRYPTED
Retrieving a secret that is outside the notbefore or expired date won't be allowed.
Permissions for secret management operations:
- get: Read a secret
- list: List the secrets or versions of a secret stored in a Key Vault
- set: Create a secret
- delete: Delete a secret
- recover: Recover a deleted secret
- backup: Back up a secret in a key vault
- restore: Restore a backed up secret to a key vault
Rotating keys - again
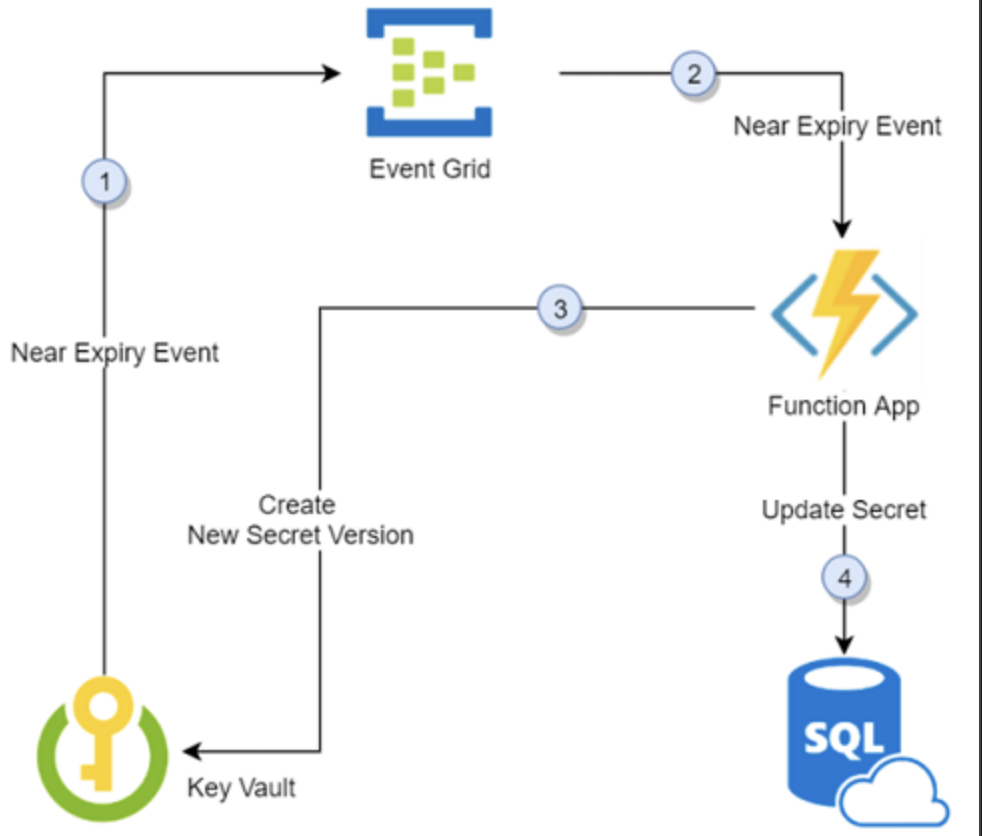
Key Vault Safety
Soft Delete enabled 7-90 days Multiple operations must be used - purge to actually delete a secret, best left to a different access role. Cannot reuse the name of a key vault if it hasn't been purged. Key vault is replicated and resilient in case of region failure. Cannot back up more than 500 versions of a secret.
Try this exercises
Explore the Azure HSM
FIPS 140-2 Level 3 requirement Best fit for lift and shift to the Azure cloud requirements.