12. Network Connectivity and Security
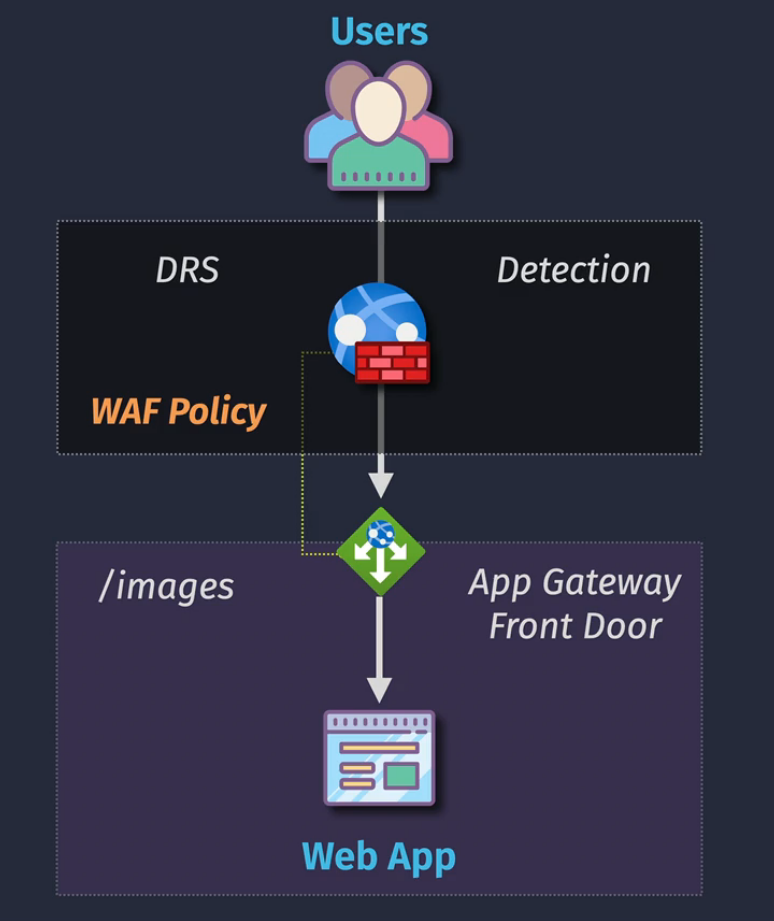
Web Application Firewalls
- Protects from OWASP threats (SQL injection, XSS
- Geographic filtering
- bot protection
- rate limiting
Components
- WAF Policy
- Settings
- Association - Front Door (global) or App Gateway (regional)
Can apply at a path level or backend
Demo - Configure a global WAF
- Create some type of load balancer
- Create a WAF policy
- not global or regional from the notes above
- Select global and select the front door tier
- Create a new RG and then set the policy mode (prevention or detection)
- You don't get access to managed rules with the Standard SKU
- Check through these and make sure you are getting the service that you want to have. You can upgrade to certain SKUs to match what you need for the WAF policy.
VNet Peering
Connecting one VNet to another VNet
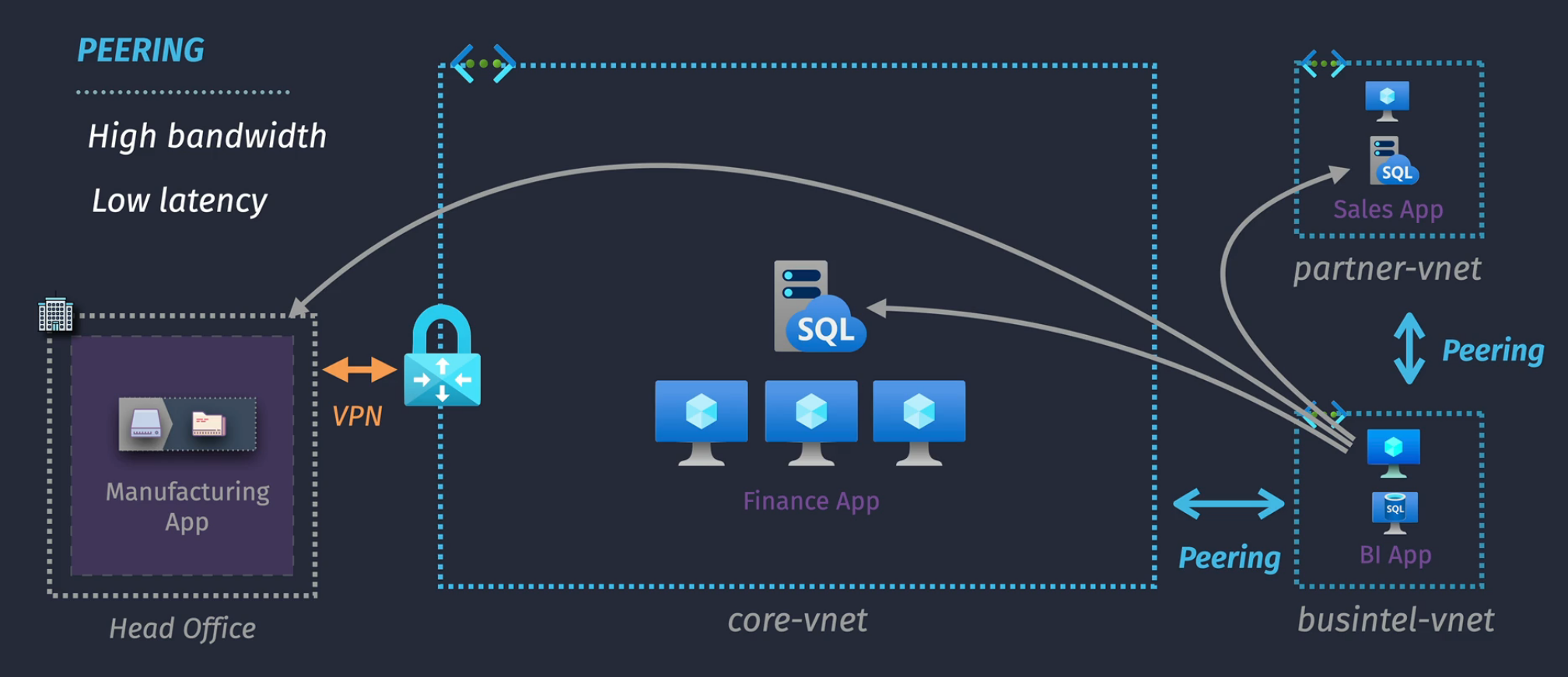
Components
Hub and spoke topology:
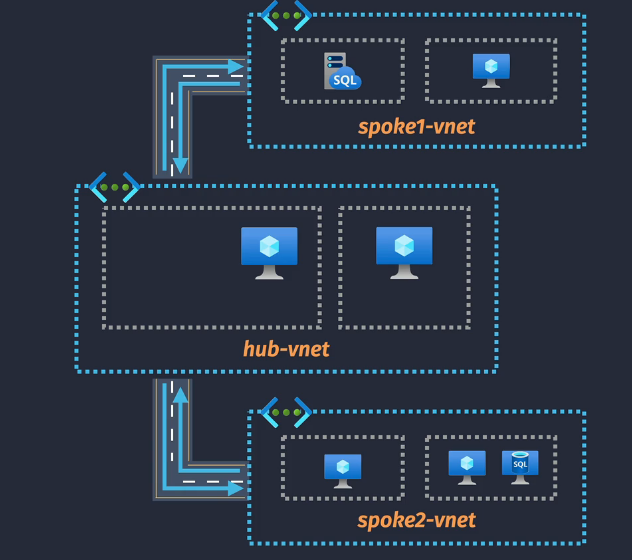 Routes - automatically updated to allow connectivity.
Routes - automatically updated to allow connectivity.
NOTE: There is no transitive routing (red line) by default.
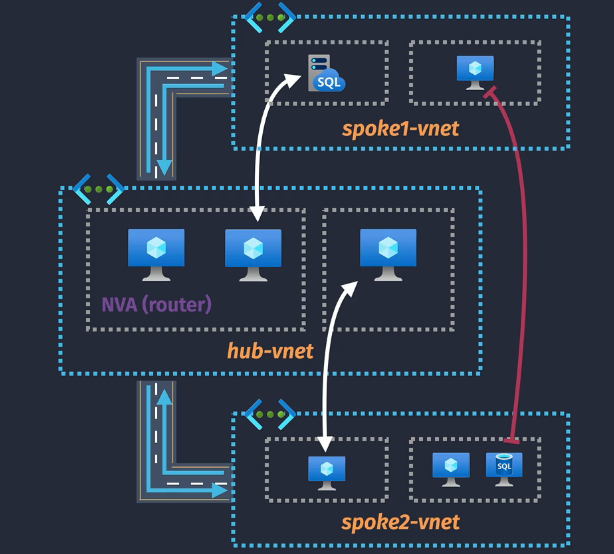
NOTE: Cannot peer overlapping IP ranges NOTE: Peering works across regions/tenants
Demo - Configure VNet Peering
- Set up two non overlapping IP range VNets and VMs: Quick Deploy: https://portal.azure.com/#create/Microsoft.Template/uri/https%3A%2F%2Fraw.githubusercontent.com%2Fjamesdplee%2Fcloudlee-click2deploy%2Fmain%2Ftemplates%2Fvm-generic.json
- Peer the VNets
- Check the settings and reference the correct settings when building your peering
- you can enter in the resource ID from a subscription that we don't have access to
- Finish peering the VNets
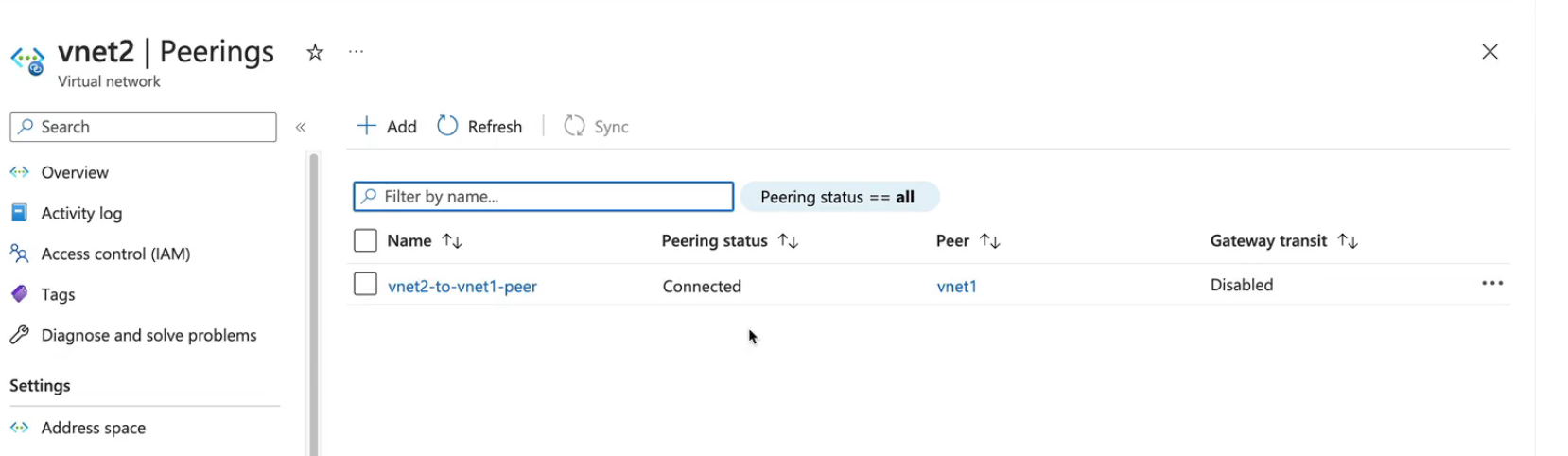
- Log into one of the VMs and try to connect to the other via the private IP
- NSG may be blocking traffic, watch out for this.
Service Endpoints
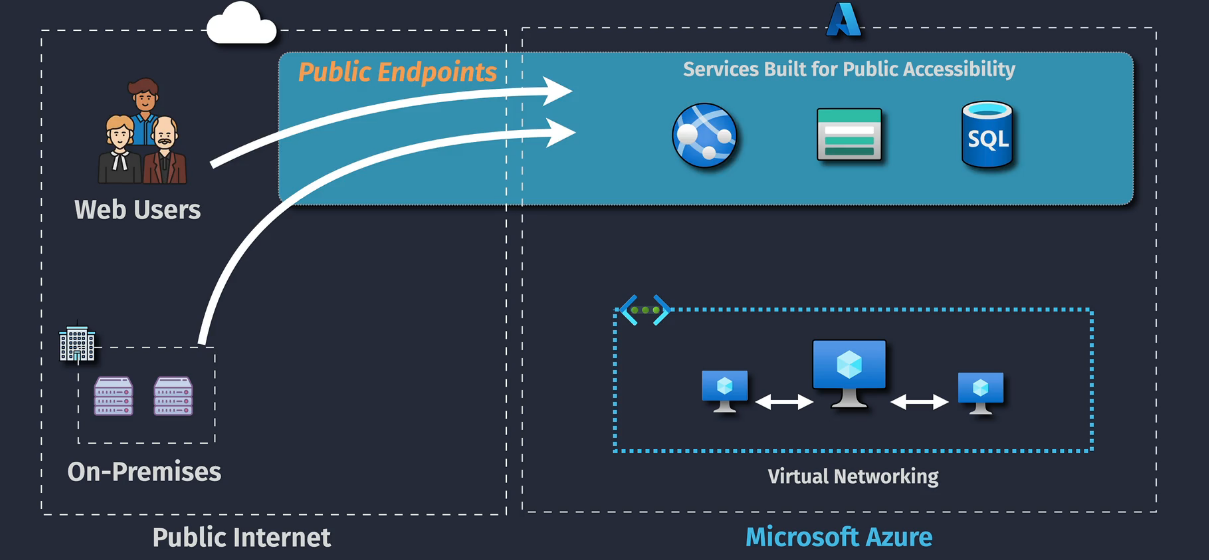
Some services are public services, SQL, Web Apps, for example.
VNets are private. A resource in the VNet needs to talk externally via a public IP address to a public endpoint to a public service....unless we use service endpoints.
Service Endpoints allow for traffic across the Microsoft Backbone
Components
Subnet Service Endpoint Routes
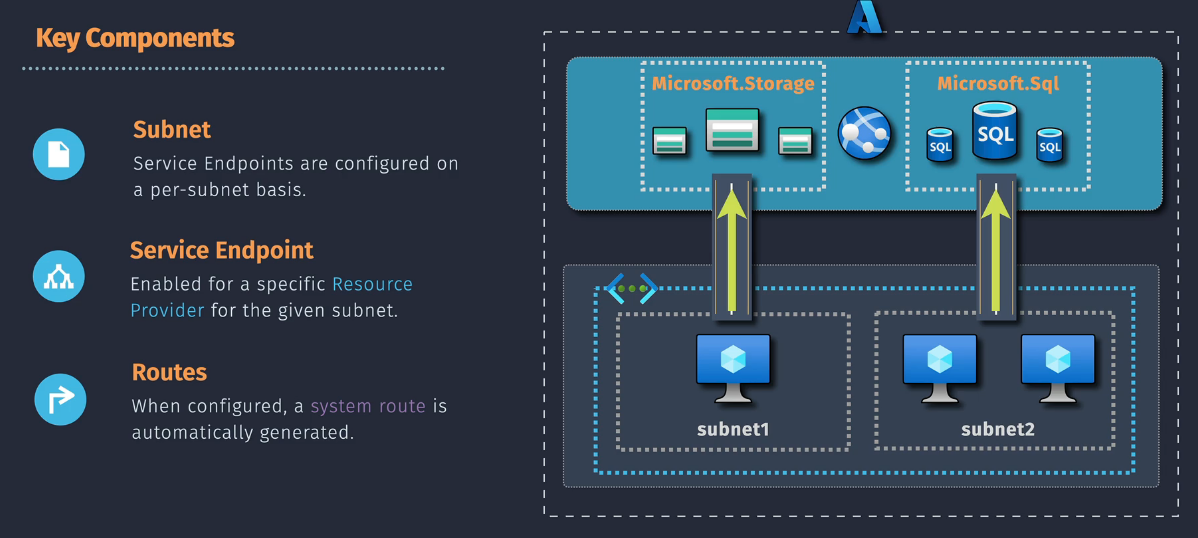
Demo - Configure a Service Endpoint for Azure Files
- Deploy these resources: https://portal.azure.com/#create/Microsoft.Template/uri/https%3A%2F%2Fraw.githubusercontent.com%2Fjamesdplee%2Fcloudlee-click2deploy%2Fmain%2Ftemplates%2Fvm-generic.json
- On the subnet, configure the service endpoint
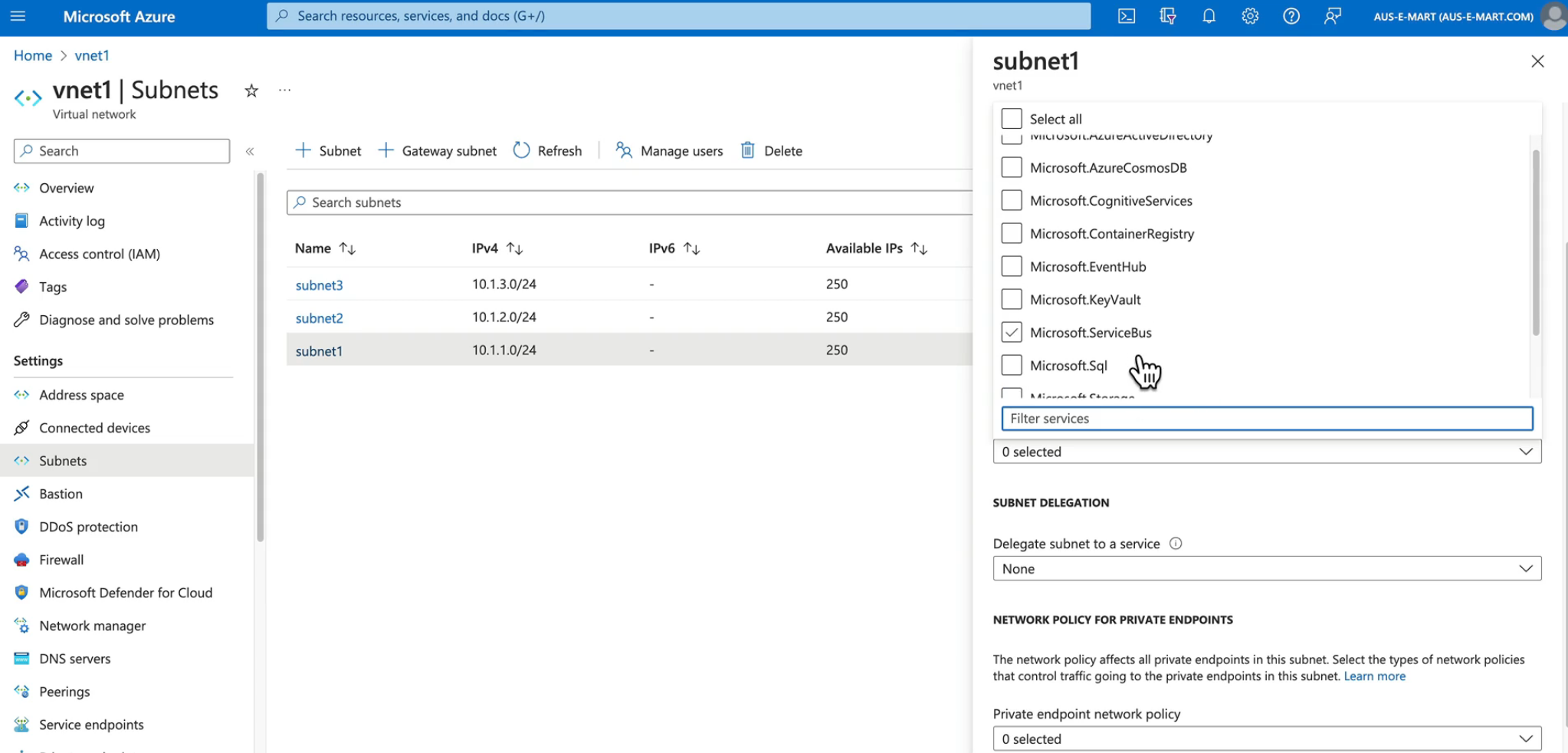
- Test the connectivity between the VMs
Private Link
This is like the Service Endpoints, but....extending them into our network.
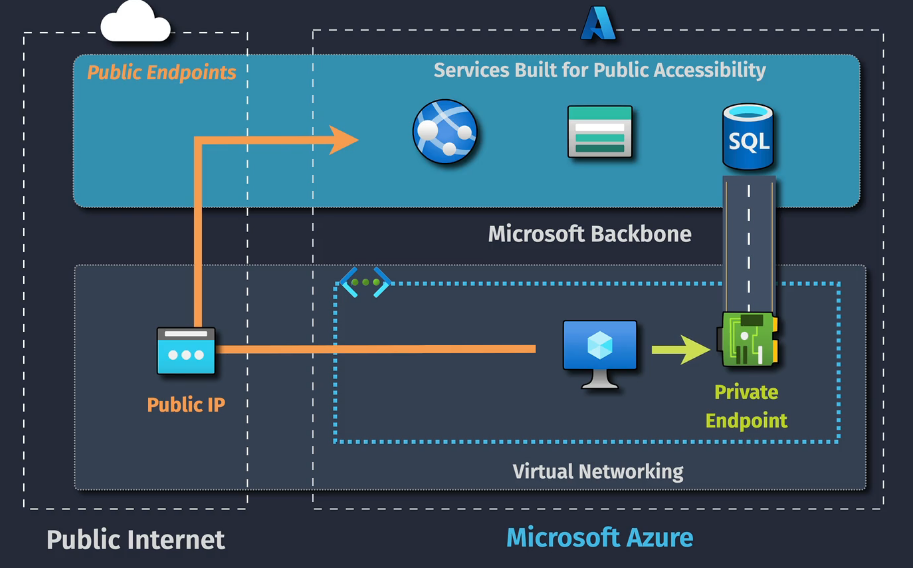
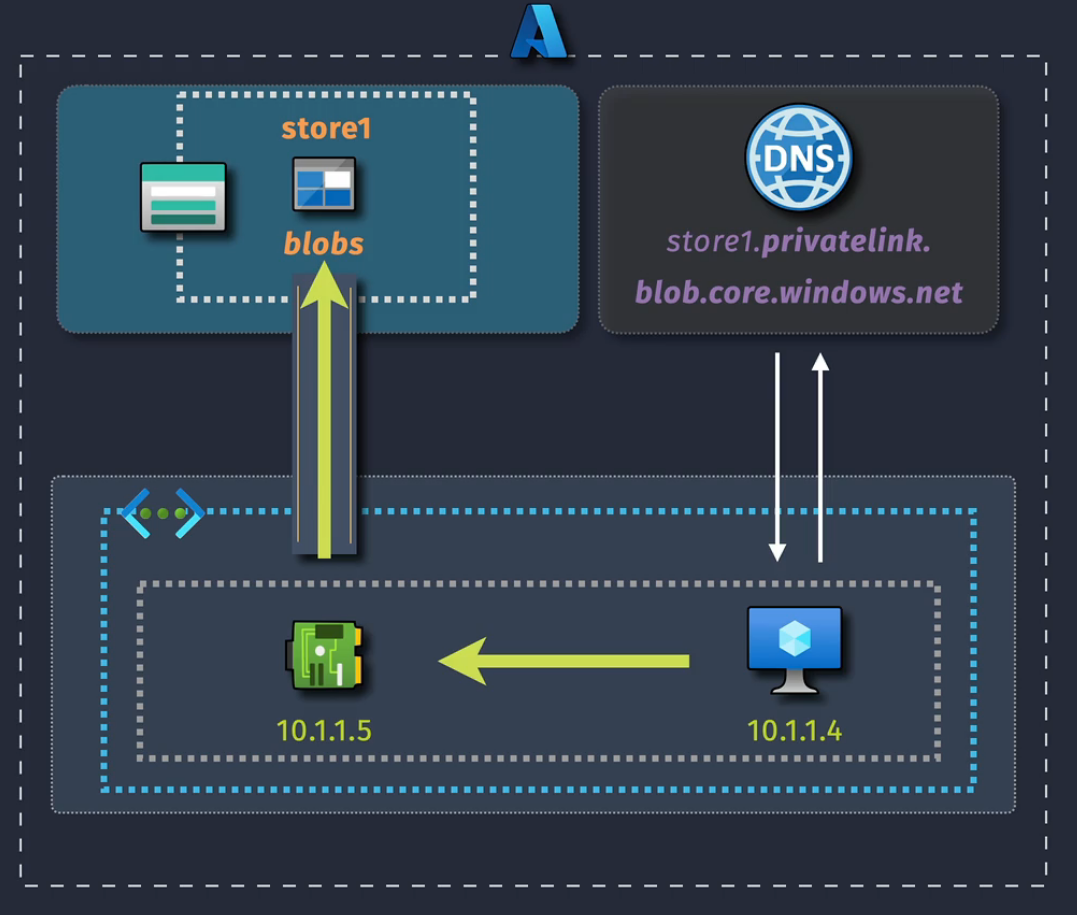
Components
Private Endpoint - The network interface that is deployed to a subnet within a VNet.
Resource - the target resource - can be a different region
IP Address - this is on our local VNet
DNS Integration - a private DNS zone will use the private IP addressing.
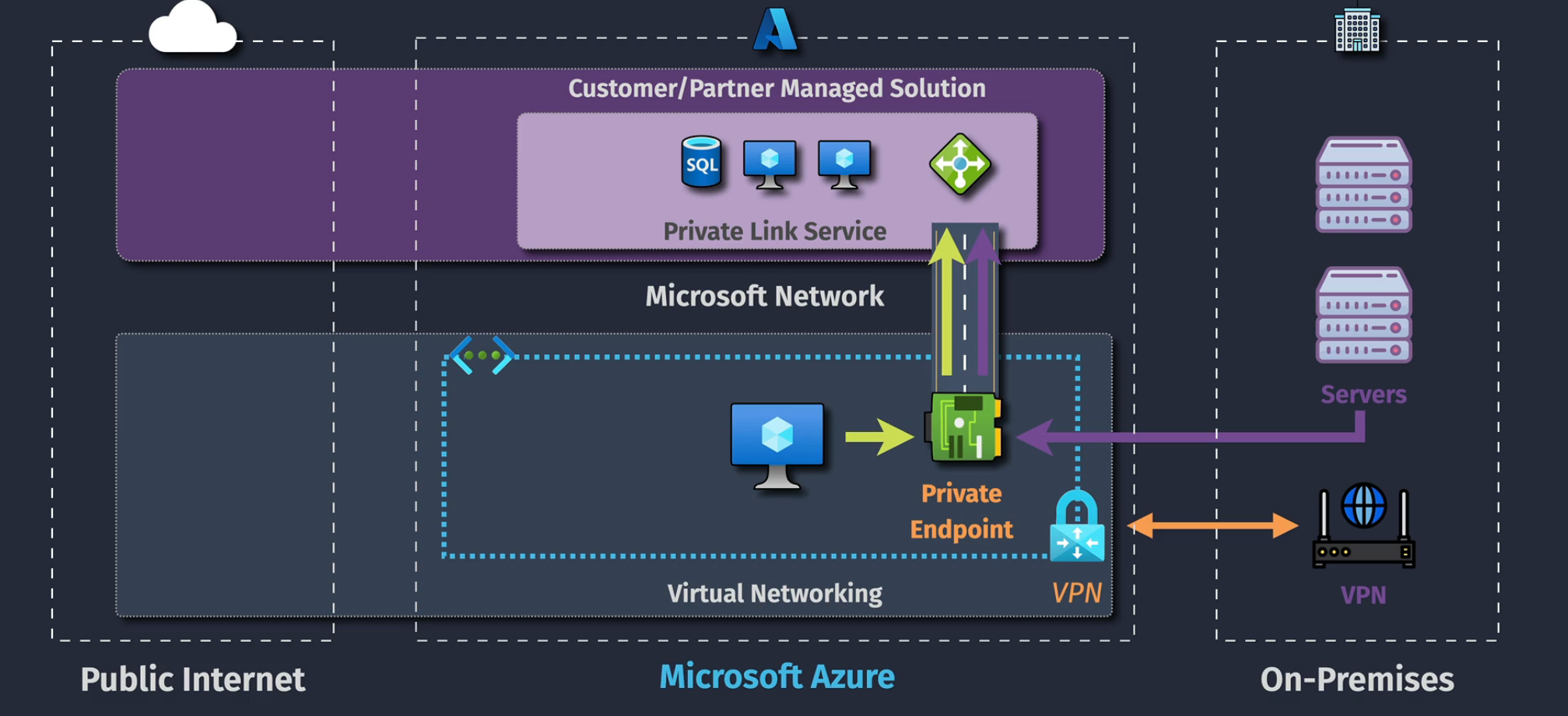
Private Link Service
Connecting to an external Azure resource outside of your tenant.
Demo - Configuring a Private Endpoint
- Deploy this: https://portal.azure.com/#create/Microsoft.Template/uri/https%3A%2F%2Fraw.githubusercontent.com%2Fjamesdplee%2Fcloudlee-click2deploy%2Fmain%2Ftemplates%2Fvm-generic.json
- Create a storage account and upload a few basic files into a file share.
- Private link Center is a fun way to manage these resources
- Click Create, give it the RG, name the PE and the nic
- Place this in the same region that the VNet lives.
- Select the resource type and then the target sub-resource
- Place this into your VNet with a static IP
- Integrate with Private DNS
- Tag the resources
- Deploy.
Connect to the VM
- Navigate into the file share and click Connect
- Grab the script and copy it and then run it in Powershell in the VM
- Do a nslookup on the DNS entry and it will return an IP on your VNet
- The public endpoint will still be the same outside of the private VNet