YAML
Key Value Pairs
name: Solomon Stroup
age: 36
hobbies:
- coding
- simracing
manager:
name: Colten Hilgendorf
age: 73
hobbies:
- golfing
manager:
Child representation:
child:
child:
child:
child:
child:
child:
child:
JSON
Also Key Value pairs
{
"name":"Solomon Stroup",
"age":36,
"hobbies":[
"coding",
"simracing"
],
"manager":{
"name":"Colten Hilgendorf",
"age":73,
"hobbies":[
"golfing"
],
"manager":null
}
}
Child Representation:
{
"child":{
"child":{
"child":{
"child":{
"child":{
"child":{
"child":null
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
# but...this takes up one line:
{"child":{"child":{"child":{"child":{"child":{"child":{"child":null}}}}}}}
Network Part 0 Intro
- Local networking - Ethernet
- Routing
- Segmenting, ports, sessions
- Applications
Best way to understand networking is to fully understand the OSI 7 Layer Model. Definition: https://osi-model.com/ Key Phrase: People don't need those stupid packets anyway. 1-7 ;)
Network Layer 1 Physical
Types:
- Ethernet Cable - The actual physical cable
- WIFI - Radio Frequencies
- Fiber - Light
Notes:
- Physical connections between places
- a Hub is needed to connect more than two devices. Anything received on one port is transmitted to all the ports - this is not a router. it doesn't route from one machine to a specific machine, nor does it act as a switch.
- No way to avoid collisions Each layer understands the layers below them, but not the ones above them. An ethernet cable doesn't understand anything because it's a Layer 1 Physical thing.
Network Layer 2 Data Link
- Frame that contains the source and destination and payload that travels across the Layer 1 physical media
- Identifies devices
- Layer 2 has a way to detect and work around collisions which can do Unicast 1:1 and Broadcast communications 1:ALL
- Switch instead of a hub which helps with collisions.
Decimal to Binary conversion (IP Addresses)
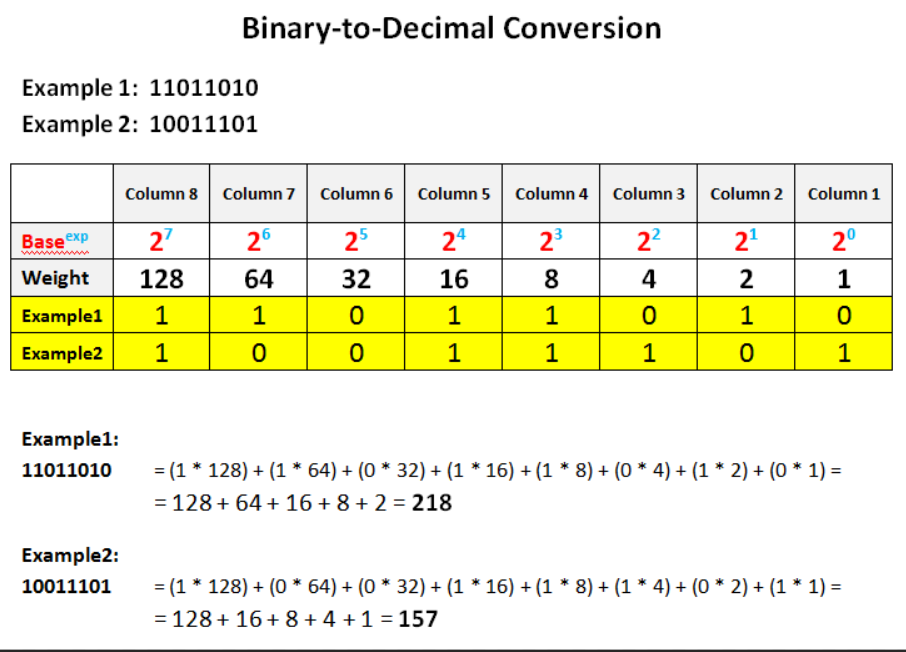
Network Layer 3 Network
- IP - the frame is then wrapped with data that says where this packet is going.
- Subnets and subnet masks
- Routes - where to forward this packet
- Route tables - multiple routes
- Router - moves packets from source to destination while encapsulating on Layer 2
- ARP - Address Resolution Protocol - sends to MAC addresses via the IP address
- Device to device communications over the Internet
- Can be delivered out of order
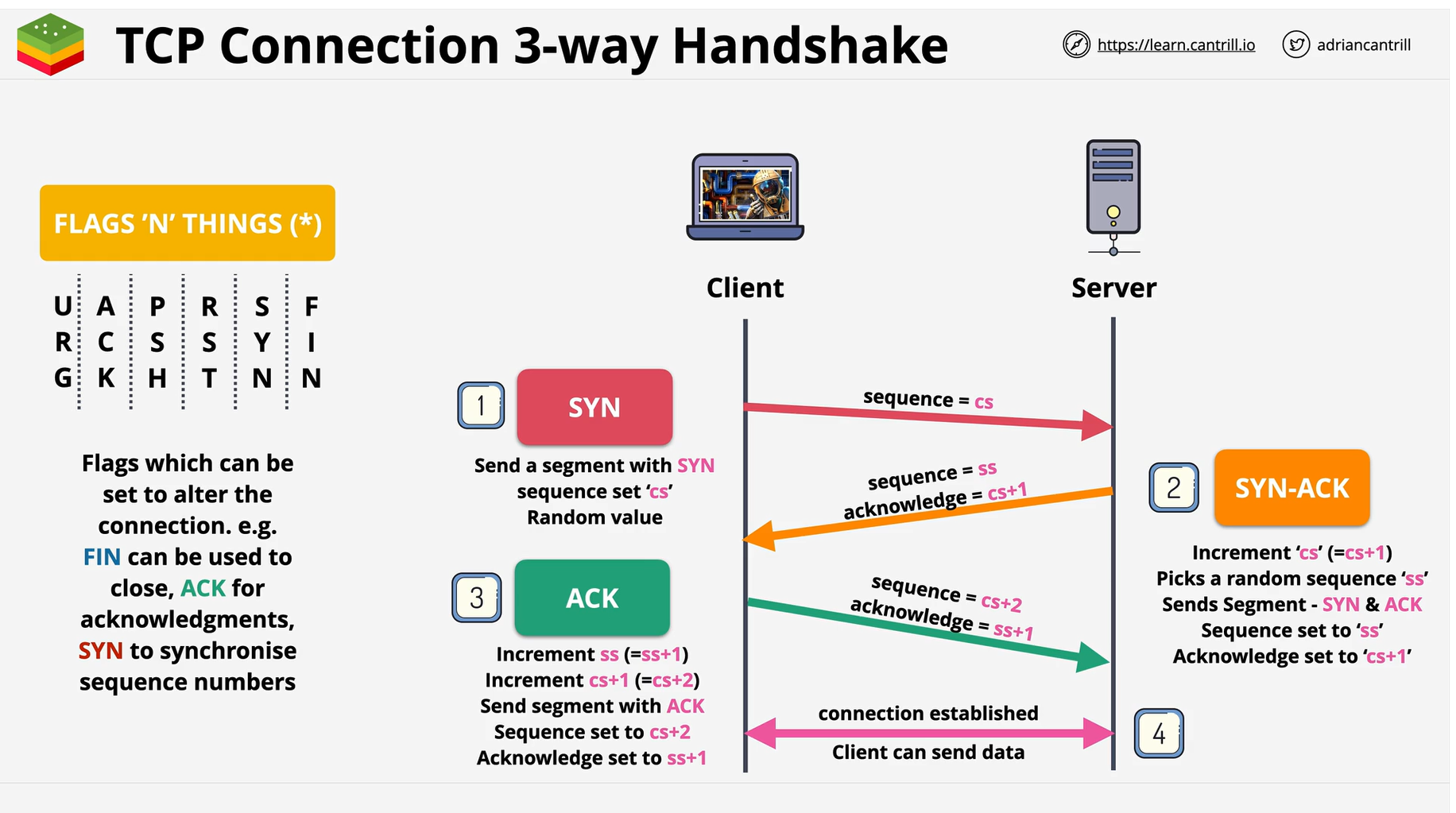
Network Layer 4 Transport and Layer 5 Session Layer
- TCP and UDP
- TCP Handshake will be used.
- Session layer 5 lies on top of Transport Layer 4.
- Ordering packets and lost packets are fixed here.
- Flow control
- Delay control
NAT
- IPv4 ONLY
- Running out of IPv4 addresses.
- This translates private IPv4 addresses into Public
- Static NAT - 1 private to 1 fixed public address (Internet Gateway)
- Dynamic NAT multiple private to multiple public addresses
- PAT Port Address Translation - MANY private to 1 Public (NAT Gateway)
Subnetting
Breaks networks up into smaller pieces.
Class A Network Class B Network Class C Network
DDOS
- designed to overload websites
- they compete against legit connections
- distributed - comes from multiple locations
- usually initiated from botnets